上一篇分析到了KeyEvent的分发其实就是把事件交给了焦点View处理,那怎么去定义一个View可获得焦点?其实很简单,只需要在xml布局中设置View的focusable属性为true就可以了,那现在就开始分析这个focusable属性究竟是怎么发挥它的作用的。
View的焦点模式
View定义了三种焦点模式,直接看它们在代码中定义:
1 | /** |
其中FOCUSABLE_MASK表示foucsable属性占用mViewFlags的bit位置,可以看出mViewFlags中第1位和第5位用来联合表示view的焦点模式,有FOCUSABLE、NOT_FOCUSABLE和FOCUSABLE_AUTO三种焦点模式,第1位控制FOCUSABLE、NOT_FOCUSABLE,第5位单独控制FOCUSABLE_AUTO.
接着看看View的构造方法中解析xml布局设置的focusable属性的过程,主要的代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39View的构造方法中
public View(Context context, AttributeSet attrs,
int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
//设置默认的值
mViewFlags = FOCUSABLE_AUTO;
// Set default values.
viewFlagValues |= FOCUSABLE_AUTO;
viewFlagMasks |= FOCUSABLE_AUTO;
......
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
//获取xml文件中设置的的焦点状态
case com.android.internal.R.styleable.View_focusable:
// (viewFlagValues & ~FOCUSABLE_MASK) 将焦点状态置为空,“与|”将从xml中获取的焦点状态赋值给viewFlagValues
viewFlagValues = (viewFlagValues & ~FOCUSABLE_MASK) | getFocusableAttribute(a);
//如果viewFlagValues中的焦点状态不再是FOCUSABLE_AUTO,说明焦点状态变了,修改位变化记录mask值
if ((viewFlagValues & FOCUSABLE_AUTO) == 0) {
viewFlagMasks |= FOCUSABLE_MASK;
}
break;
}
.......
if (viewFlagMasks != 0) {
setFlags(viewFlagValues, viewFlagMasks);
}
}
//将xml中设置的焦点状态转换为View自己定义的二进制格式
private int getFocusableAttribute(TypedArray attributes) {
TypedValue val = new TypedValue();
if (attributes.getValue(com.android.internal.R.styleable.View_focusable, val)) {
if (val.type == TypedValue.TYPE_INT_BOOLEAN) {
return (val.data == 0 ? NOT_FOCUSABLE : FOCUSABLE);
} else {
return val.data;
}
} else {
return FOCUSABLE_AUTO;
}
}
在最开始的时候设置了View的焦点模式为FOCUSABLE_AUTO,在遍历属性时如果xml布局有设置focusable属性,则取出,没有的话依然是FOCUSABLE_AUTO,这样focuable属性就转换成了viewFlagValues中的参数,构造方法最后还调用了setFlags方法设置mViewFlags,这个方法内还处理设置了clickable但没有设置focusable的情况,如下:
1 | View中 |
可以看出,如果是FOCUSABLE_AUTO情况,也就是xml文件没设置focusable属性,焦点的模式还与clickable属性有关,如果View是clickable的,那么View是FOCUSABLE,否则是NOT_FOCUSABLE,可以用下面这张表来描述clickable和focusable属性对View的焦点模式的影响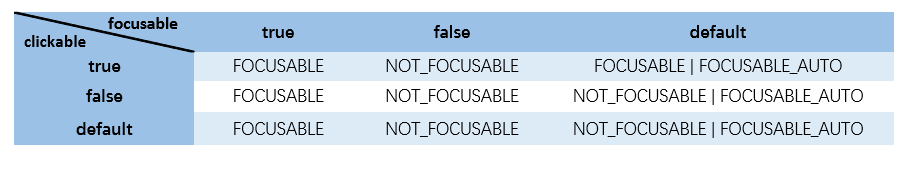
现在可以回答上一篇结束时提的问题了,Android手机应用运行在Android电视上可以响应按键事件吗?如果这个View在xml文件中设置了clickable属性为true那这个View就可以获得焦点,也就可以响应按键事件,如果既没有设置clickable也没有设置focusable为true,那这个View就获取不到焦点,也就响应不了按键事件了。
下面是View提供的两种获得焦点模式的方法
1 | View中 |
一般情况我们使用isFocusable方法就OK了,getFocusable方法可以用来在可以获得焦点时判断是clickable导致的,还是focusable设置的.
ViewGroup的焦点模式
上小节分析的View的焦点模式完全适用于ViewGroup,毕竟它也是View的儿子,但由于ViewGroup有子View,为了避免焦点产生歧义,还定义了ViewGroup相对于子View的三种获得焦点的顺序,如下:
1 | /** |
ViewGroup的FLAG_MASK_FOCUSABILITY是用来控制焦点在View树中的传递顺序的,顺序有三种:
- FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS: 在所有子View之前,自己没获取再给子View
- FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS: 在所有子View之后,所有子View都没能获得焦点才问下自己能不能
- FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS: 不通知子View ,即使自己获取不到
和View的焦点模式一样,获得焦点的顺序也是在构造方法中设置的:
1 | ViewGroup中 |
从代码中可以发现,如果不写这个属性,ViewGroup设置自己在所有子View之前处理焦点.
View的requestFocus方法
要让一个View获得焦点,需要调用它的requestFocus方法,调用时序图如下(具体的方法可以直接搜索源码):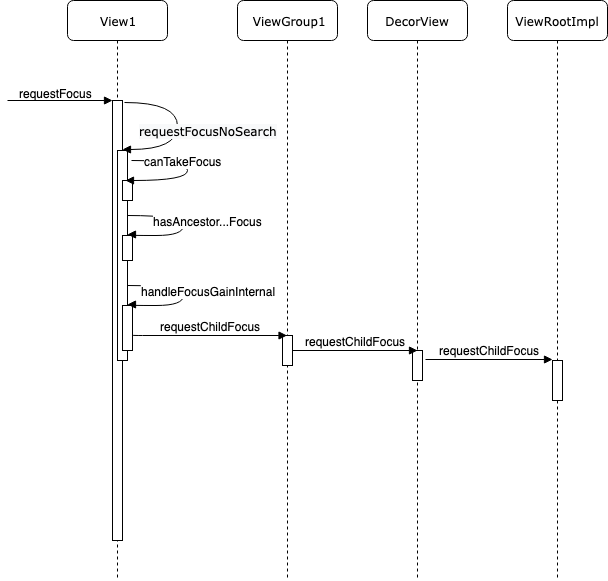
View先调用自己的canTakeFocus方法确认自己是不是能够获得焦点,这个方法如下:
1 | private boolean canTakeFocus() { |
判断的依据是 : 1.view可见 2.可以获得焦点 3.是enable的 4.有大小
然后递归调用所有父View的hasAncestorThatBlocksDescendantFocus方法,确认父View是不是设置了拦截焦点,如果父View拦截了焦点,自己就不能获得焦点。
如果上面两项都通过了,那就可以名正言顺的获得焦点了,handleFocusGainInternal方法如下:
1 | void handleFocusGainInternal( int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) { |
方法中将mPrivateFlags中的表示是否有焦点的bit置为1,表示自己有焦点,这在上一章中分析过,之后调用父View的requestChildFocus的方法,如下:
1 |
|
父View的requestChildFocus方法中将mFocused成员变量指向这个有焦点的View,然后通知自己的父View我是那个包含焦点View的子View,如此遍历所有的父View,直到ViewRootImpl,这样就修改所有的父View中的mFocused变量了,之后有按键事件时就按这个路径传递KeyEvent,这也在上一篇中也有分析。
ViewGroup的requestFocus方法
ViewGroup复写了View的requestFocus(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect)方法,如下:
1 |
|
在这个方法中ViewGroup根据自己相对子View获得焦点的顺序来确认调用方法的顺序。从代码中可以看出如果一个ViewGroup要获得焦点它的逻辑和View是一样的,而且由于ViewGroup默认设置了FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS,如果它再设置focusable为true,它的想获得焦点的儿子们就不要指望爸爸主动给焦点了😂,只能通过自己的requestFocus去获得。
总结
简短总结一下本篇的内容:
- View的焦点模式可以使用focusable属性定义,也与clickable属性有关联
- ViewGroup在View的基础上定义了自己相对于子View的处理焦点的顺序
- View通过requestFocus方法获得焦点
- ViewGroup复写了requestFocus方法,加入了顺序判断
到这里按键事件的分发和获得焦点的过程分析完毕,但事情还没完,当按下按键时会发现焦点会在View之间移动,那按键事件是怎么转换为焦点View的变化的呢?请看下篇分析: Android TV开发按键与焦点深入解析(三)–按键事件转换成焦点移动的过程