Matrix检测主线程耗时方法
Matrix是一个开源的全方面监控应用性能的工具,它的一个功能是能检测Android应用的主线程的耗时方法,比如我们设置耗时阈值为700ms,那么基于Looper机制运行的主线程中如果存在一个Message的执行时间超过700ms,它可以直接统计出这个Message调用的方法栈,并且可以大致统计出每个被调用方法的执行时间,这样我们就可以愉快地发现导致主线程耗时的方法了。
具体的实现方式可以看官方介绍
一个idea
实际上我们使用Matrix的初衷和作者还不太一样,官方介绍侧重于怎样去监控线上的卡顿耗时方法,而我们知道要搭建一个这样的监控闭环是需要投入的,即使有Matrix这个工具作为基础,小团队也没有这个精力去搭建前后端一体的监控系统。所以实际上对于大部分开发者,也就是开发时玩玩,帮助检测下性能情况。基于作者的初衷,我们可以看到在有耗时方法时它会打印这样的日志:
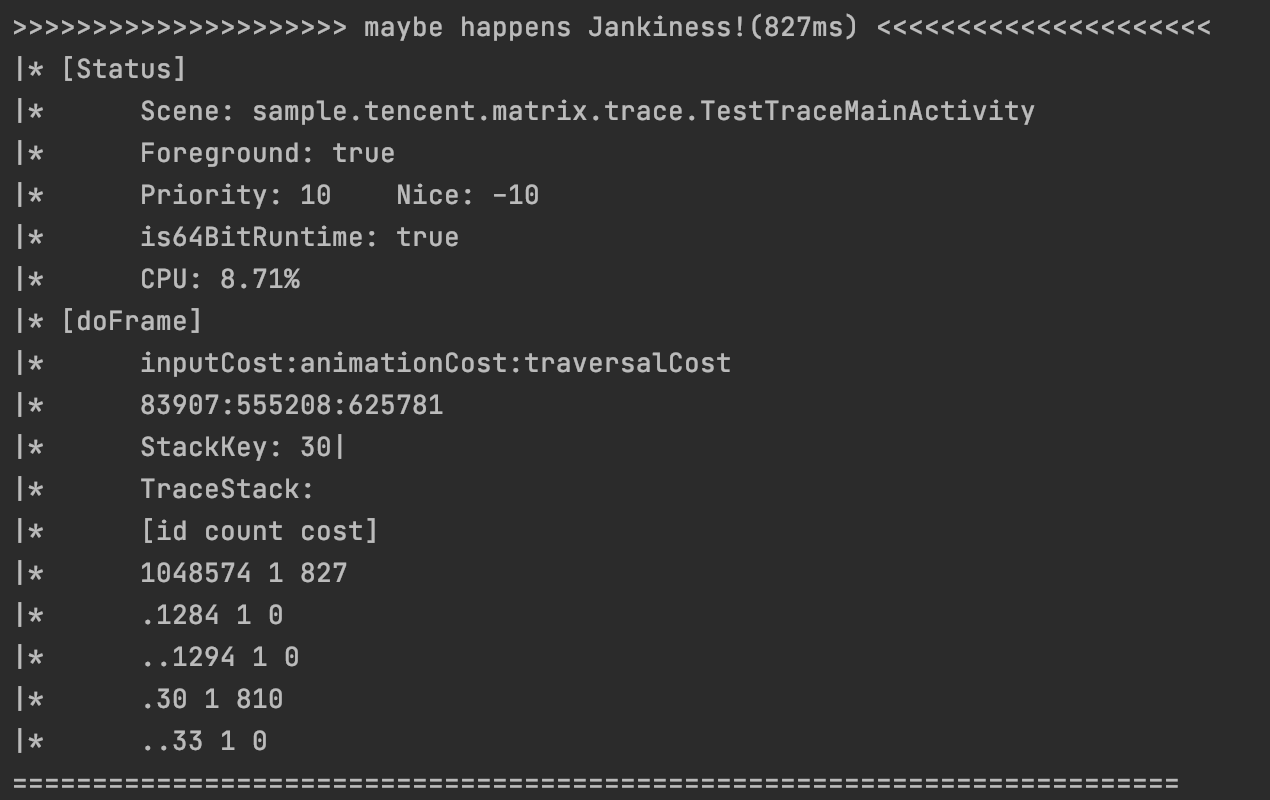
为什么调用方法栈是一堆数字呢?这是因为实际上它会被传到服务器,服务器再根据当时编译生成的methodMapping.txt文件将数字id替换成对应的方法名字,这样就可以看到具体的方法名字以及耗时了。
但是开发时我就想立马看看是哪个方法导致耗时的,可不可以直接打印耗时方法到Logcat?细想一下是可以的,编译一次,每个方法id被插入到本次编译的的每个方法中,id对应的方法名会被记录到了电脑本地的methodMapping.txt中,我们直接把这个methodMapping.txt也保存进apk里面,然后在运行时将id对应的方法名保存进一个HashMap,这样一旦有耗时就可以根据id找到每个方法名字,然后打印出来,就可以实时显示哪个方法耗时了。
实现方法
整个实现的困难的地方是怎么将编译阶段生成的methodMapping.txt拷贝进生成apk的assets目录下,第一个想到是在编译的时候methodMapping.txt会被生成存放在build/outputs/mapping/debug目录下,直接写一个task将这个目录下的这个文件拷贝进工程的assets目录等待打包apk就完事了,但是实践下来不太对,下面是编译的task日志:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| Executing tasks: [:app:assembleDebug]
> Configure project :app
[I][Matrix.TraceInjection] Using trace transform mode.
> Task :app:cleanBuildDirTask
Clean app bulid dir before assemble
> Task :app:preBuild UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:preDebugBuild UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:compileDebugAidl NO-SOURCE
> Task :app:compileDebugRenderscript NO-SOURCE
> Task :app:generateDebugBuildConfig
> Task :app:checkDebugAarMetadata
> Task :app:generateDebugResValues
> Task :app:generateDebugResources
> Task :app:createDebugCompatibleScreenManifests
> Task :app:extractDeepLinksDebug
> Task :app:processDebugMainManifest
> Task :app:processDebugManifest
> Task :app:javaPreCompileDebug
> Task :app:generateJsonModelDebug
> Task :app:externalNativeBuildDebug
> Task :app:mergeDebugNativeDebugMetadata NO-SOURCE
> Task :app:mergeDebugShaders
> Task :app:compileDebugShaders NO-SOURCE
> Task :app:generateDebugAssets UP-TO-DATE
> Task :app:mergeDebugAssets
> Task :app:processDebugManifestForPackage
> Task :app:processDebugJavaRes NO-SOURCE
> Task :app:mergeDebugResources
> Task :app:processDebugResources
> Task :app:compileDebugJavaWithJavac
> Task :app:compileDebugSources
> Task :app:transformClassesWithMatrixTraceTransformForDebug
[I][Matrix.Trace] [doTransform] Step(1)[Parse]... cost:22ms
[I][Matrix.Trace] [doTransform] Step(2)[Collection]... cost:262ms
[I][Matrix.Trace] [doTransform] Step(3)[Trace]... cost:1081ms
[I][Matrix.TraceTransform] Insert matrix trace instrumentations cost time: 1367ms.
> Task :app:dexBuilderDebug
> Task :app:mergeDebugJniLibFolders
> Task :app:checkDebugDuplicateClasses
> Task :app:mergeDebugJavaResource
> Task :app:compressDebugAssets
> Task :app:mergeExtDexDebug
> Task :app:validateSigningDebug
> Task :app:mergeLibDexDebug
> Task :app:mergeDebugNativeLibs
> Task :app:stripDebugDebugSymbols
> Task :app:mergeProjectDexDebug
> Task :app:packageDebug
> Task :app:assembleDebug
BUILD SUCCESSFUL in 21s
31 actionable tasks: 31 executed
|
生成methodMapping.txt的task是transformClassesWithMatrixTraceTransformForDebug,而移动assets目录下的文件到指定的打包目录下的task是mergeDebugAssets,这个task是要先于transformClassesWithMatrixTraceTransformForDebug的,所以要么第一次打包找不到本地methodMapping.txt,要么第二次打包拿到的是上次编译的,总之都不对。所以需要写一个拷贝methodMapping.txt的task在transformClassesWithMatrixTraceTransformForDebug之后、在打包apk之前执行,这就可以保证每次拷贝的都是本次编译生成的methodMapping.txt。当然由于plugin的源码我们都有,也可以直接修改 transformClassesWithMatrixTraceTransformForDebug,在里面直接写这个逻辑,这里只介绍写单独的task。
我参考了compressDebugAssets这个task,整体的编译打包apk的流程没太搞明白,但是知道在执行packageDebug之前它会调用compressDebugAssets将所有merged_assets下的文件压缩拷贝到build/intermediates/compressed_assets/debug/out/assets下,之后packageDebug再到这个目录下取文件放到apk的assets目录下。
控制task运行顺序
gradle提供了一个task依赖另外一个task的方法dependsOn,也提供mustRunAfter这个方法让task在某个task之后执行,我们就可以利用这个两个方法,让task在某两个方法之间运行,修改matrix-gradle-plugin模块下MatrixTraceInjection.kt的方法,让在插桩完成生成methodMapping.txt之后执行我们自己的task,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| private fun doInjection(appExtension:AppExtension,
project:Project,
extension:MatrixTraceExtension) {
appExtension.applicationVariants.all {
variant ->
val variantName = variant.name
if (injectTaskOrTransform(project, extension, variant) == InjectionMode.TransformInjection) {
transformInjection()
val action = CopyMethodMappingTask.CreationAction(CreationConfig(variant, project), extension, variant.packageApplication)
val taskProvider = project.tasks.register(action.name, action.type, action)
BaseCreationAction.findNamedTask(project.tasks, computeTaskName("package", variantName, "")) ?.
configure {
it.dependsOn(taskProvider)
}
val transformClassesTaskName = computeTaskName("transformClassesWith${MatrixTraceTransform.TASK_NAME}For", variantName, "")
val transformClassesTaskProvider = BaseCreationAction.findNamedTask(project.tasks, transformClassesTaskName)
taskProvider.configure {
it.mustRunAfter(transformClassesTaskProvider)
}
} else {
taskInjection(project, extension, variant)
}
}
}
|
只实现了AGP 4.0版本之后的逻辑,3.6版本没实现哦。
copyDebugMethodMappingToAssets Task
matrix-gradle-plugin有其他的task实现,可以照猫画虎写自己的task,目标就是将methodMapping.txt压缩并拷贝到build/intermediates/compressed_assets/debug/out/assets下,具体的逻辑就不文字介绍了,全部代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
| package com.tencent.matrix.plugin.task
import com.android.build.gradle.tasks.PackageAndroidArtifact
import com.android.builder.model.AndroidProject
import com.android.utils.FileUtils
import com.google.common.base.Joiner
import com.tencent.matrix.javalib.util.FileUtil
import com.tencent.matrix.javalib.util.Log
import com.tencent.matrix.plugin.compat.CreationConfig
import com.tencent.matrix.plugin.trace.MatrixTraceInjection
import com.tencent.matrix.trace.Configuration
import com.tencent.matrix.trace.extension.MatrixTraceExtension
import org.gradle.api.Action
import org.gradle.api.DefaultTask
import org.gradle.api.tasks.TaskAction
import org.gradle.work.InputChanges
import java.io.File
import java.io.FileInputStream
import java.io.FileOutputStream
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry
import java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream
abstract class CopyMethodMappingTask : DefaultTask() {
private lateinit var config: Configuration
private lateinit var destinationDirFile: File
fun initOutputs() {
outputs.dir(destinationDirFile)
}
@TaskAction
fun execute(inputChanges: InputChanges) {
val sourceFile = File(config.methodMapFilePath)
val zipFileDir = File(config.mappingDir, "method")
if (!zipFileDir.exists()) {
zipFileDir.mkdirs()
}
val zipFile = File(zipFileDir, "methodMapping.zip")
if (!zipFile.exists()) {
zipFile.createNewFile()
}
val fos = FileOutputStream(zipFile)
val zos = ZipOutputStream(fos)
val fis = FileInputStream(sourceFile)
try {
val e = ZipEntry("assets/methodMapping.txt")
zos.putNextEntry(e)
val buffer = ByteArray(FileUtil.BUFFER_SIZE)
var len: Int
while (fis.read(buffer).also { len = it } > 0) {
zos.write(buffer, 0, len)
}
fis.close()
zos.close()
fos.close()
} finally {
FileUtil.closeQuietly(fis)
FileUtil.closeQuietly(zos)
FileUtil.closeQuietly(fos)
}
Log.i(MatrixTraceInjection.TAG, "source assets path:${zipFileDir.absolutePath}")
Log.i(MatrixTraceInjection.TAG, "destination assets path:${destinationDirFile.absolutePath}")
FileUtils.copyFileToDirectory(zipFile, destinationDirFile)
}
class CreationAction(private val creationConfig: CreationConfig,
private val extension: MatrixTraceExtension,
private val packageAndroidArtifact: PackageAndroidArtifact)
: Action<CopyMethodMappingTask>, BaseCreationAction<CopyMethodMappingTask>(creationConfig) {
override val name = computeTaskName("copy", "MethodMappingToAssets")
override val type = CopyMethodMappingTask::class.java
override fun execute(task: CopyMethodMappingTask) {
task.config = configure(creationConfig, packageAndroidArtifact)
task.destinationDirFile = File(packageAndroidArtifact.assets.asFile.get(), "assets")
task.initOutputs()
}
private fun configure(creationConfig: CreationConfig, packageAndroidArtifact: PackageAndroidArtifact): Configuration {
val buildDir = creationConfig.project.buildDir.absoluteFile
val dirName = packageAndroidArtifact.variantName
val mappingOut = Joiner.on(File.separatorChar).join(buildDir, AndroidProject.FD_OUTPUTS, "mapping", dirName)
return Configuration.Builder().setBaseMethodMap(extension.baseMethodMapFile)
.setBlockListFile(extension.blackListFile)
.setMethodMapFilePath("$mappingOut/methodMapping.txt")
.setIgnoreMethodMapFilePath("$mappingOut/ignoreMethodMapping.txt")
.setMappingPath(mappingOut)
.build()
}
}
}
|
APP端的代码
上面只是讲了怎么将methodMapping.txt拷贝进apk,这里介绍下怎样解析打印日志(这个就简单的多啦~)。
Matrix提供了com.tencent.matrix.plugin.PluginListener 这个接口用于开发者处理检测到的异常信息,我们可以直接实现接口,当收到耗时慢方法的Issue时,将assets下的methodMapping.txt解析成键值对,然后再根据id打印找到方法名并打印,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
@Override
public void onReportIssue(final Issue issue) {
MatrixLog.e(TAG, issue.toString());
if (issue.getTag().equals(SharePluginInfo.TAG_PLUGIN_EVIL_METHOD)) {
if (!isInitMethodMap) {
try (InputStream inputStream = softReference.get().getAssets().open("methodMapping.txt");
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
) {
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
String[] info = line.split(",");
methodMap.put(Integer.valueOf(info[0]), info[2]);
}
isInitMethodMap = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (isInitMethodMap) {
JSONObject jsonObject = issue.getContent();
try {
String scene = jsonObject.get(SharePluginInfo.ISSUE_SCENE).toString();
String cpuUsage = jsonObject.getString(SharePluginInfo.ISSUE_CPU_USAGE);
String traceStack = jsonObject.getString(SharePluginInfo.ISSUE_TRACE_STACK);
String cost = jsonObject.getString(SharePluginInfo.ISSUE_COST);
MatrixLog.e(TAG, ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> slow method log start >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "|*[Status]");
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "|*\tScene: " + scene);
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "|*\tCPU: " + cpuUsage);
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "|*\tCost: " + cost + "ms");
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "|*[doFrame]");
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "|* TraceStack:");
String[] lines = null;
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(traceStack) && ((lines = traceStack.split(System.lineSeparator())) != null)) {
for (int i = 0; i < lines.length; i++) {
String line = lines[i];
StringBuilder lineBuilder = new StringBuilder();
String[] messages = line.split(",");
int dotCount = Integer.parseInt(messages[0]);
int methodId = Integer.parseInt(messages[1]);
int repeat = Integer.parseInt(messages[2]);
String methodCost = messages[3] + "ms";
StringBuilder dotBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int j = 0; j < dotCount; j++) {
dotBuilder.append(".");
}
for (int j = 0; j < repeat; j++) {
String method = methodMap.get(methodId);
lineBuilder.append("|*\t").append(dotBuilder).append(method).append(" ").append(methodCost).append("\n");
}
MatrixLog.e(TAG, lineBuilder.toString());
}
}
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< slow method log end <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<");
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
|
设置慢方法阈值为700ms,以在Activity的onCreate方法中睡眠750ms为例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.test_trace);
SystemClock.sleep(750);
}
|
实时打印的日志如下:
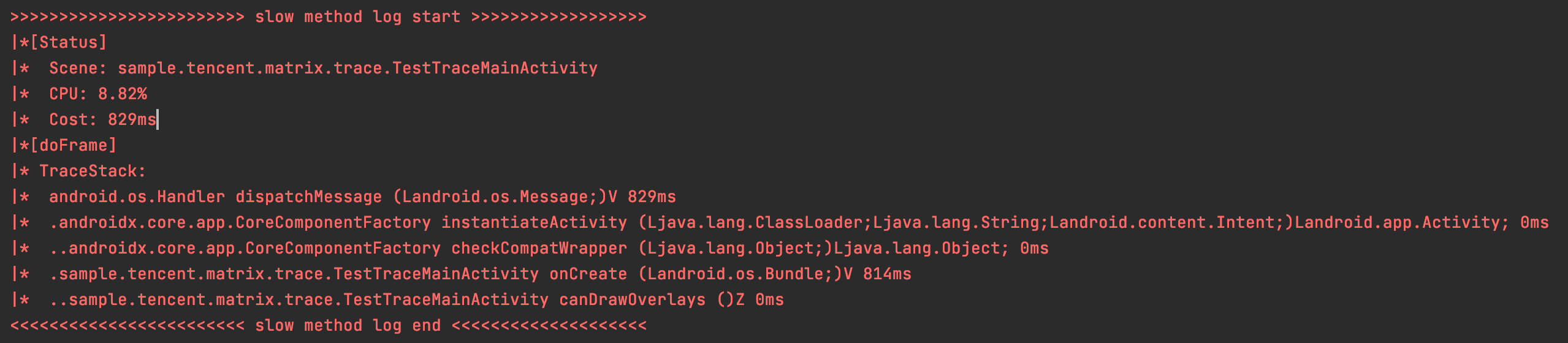
可以看到这个Message中,是onCreate这个方法执行耗时了大概800多毫秒,这时再去找到代码中的这个方法,排查哪行代码耗时。
其他
实际上我们在开发阶段检测卡顿还有其他比较方便的方式,比如使用Android Studio的Profiler、直接抓systrace。这个方法只能算是一种比较主动的方式吧,而且并不如Profiler容易上手,使用时应该考虑实际情况。

